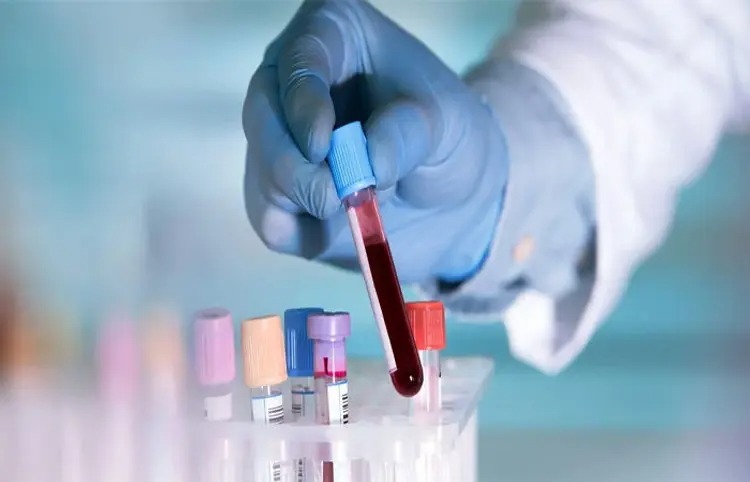
Bengaluru: Strand Life Sciences, a subsidiary of Reliance Industries Limited, has launched CancerSpot, a new blood test for early detection of various types of cancer. The test will use modern methylation profiling technology to identify tumor DNA residues in blood samples. Designed for proactive and routine screening, CancerSpot’s genome sequencing and analysis process detects DNA methylation signals specific to cancer, which may prove useful for people of different ancestries.
Reliance Industries board member Isha Ambani Piramal stressed the importance of testing, citing rising cancer cases in India. Citing the enormous economic, social and psychological stress of cancer, he described CancerSpot as Reliance’s commitment to launching medical breakthroughs. He said genomics-based testing like CancerSpot is emblematic of the company’s ‘WeCare’ policy that focuses on improving global health and well-being.
At the launch of Strand’s state-of-the-art Genomics Diagnostics and Research Center in Bengaluru, Dr. Ramesh Hariharan, CEO and Co-Founder, Strand Life Sciences, emphasized the importance of early diagnosis of cancer. He described CancerSpot as an effort to empower individuals to be at the forefront of the fight against the disease after years of research. The strand’s 24-year legacy in genomics innovation is a first for India.
The newly opened research center will play a key role in launching the CancerSpot initiative which will support research to deliver life-saving diagnoses. This strand will help in introducing genomics and meeting the need of cancer diagnosis for Indian and global population.
Drug-resistant pneumonia kills 2 million people worldwide every year
First indigenous antibiotic launched in India for drug resistant infections
BIRAC researchers develop drug ten times more powerful
New Delhi: India has launched the first indigenous antibiotic for drug-resistant infections. The drug named Napithromycin has been developed by researchers at the Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC), Department of Biotechnology, India.
Naphthromycin is used in the treatment of drug-resistant community-acquired bacterial pneumonia (CABP) in adults.
In the race to develop replacement antibiotics and antifungals, the soft launch of nafithromycin is a step forward towards ending the epidemic of antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
Drug-resistant pneumonia kills two million people worldwide every year. India accounts for 23 percent of global community pneumonia cases. And it is facing challenges of treatment. This includes increasing resistance to drugs such as azithromycin. Azithromycin has been the primary treatment for pneumonia for many years because it targets the bacteria responsible for the development of the disease.
This medicine is given in a dose of 500 mg for three to ten days. The dosage is increased depending on the severity of the condition.
 look news india
look news india
