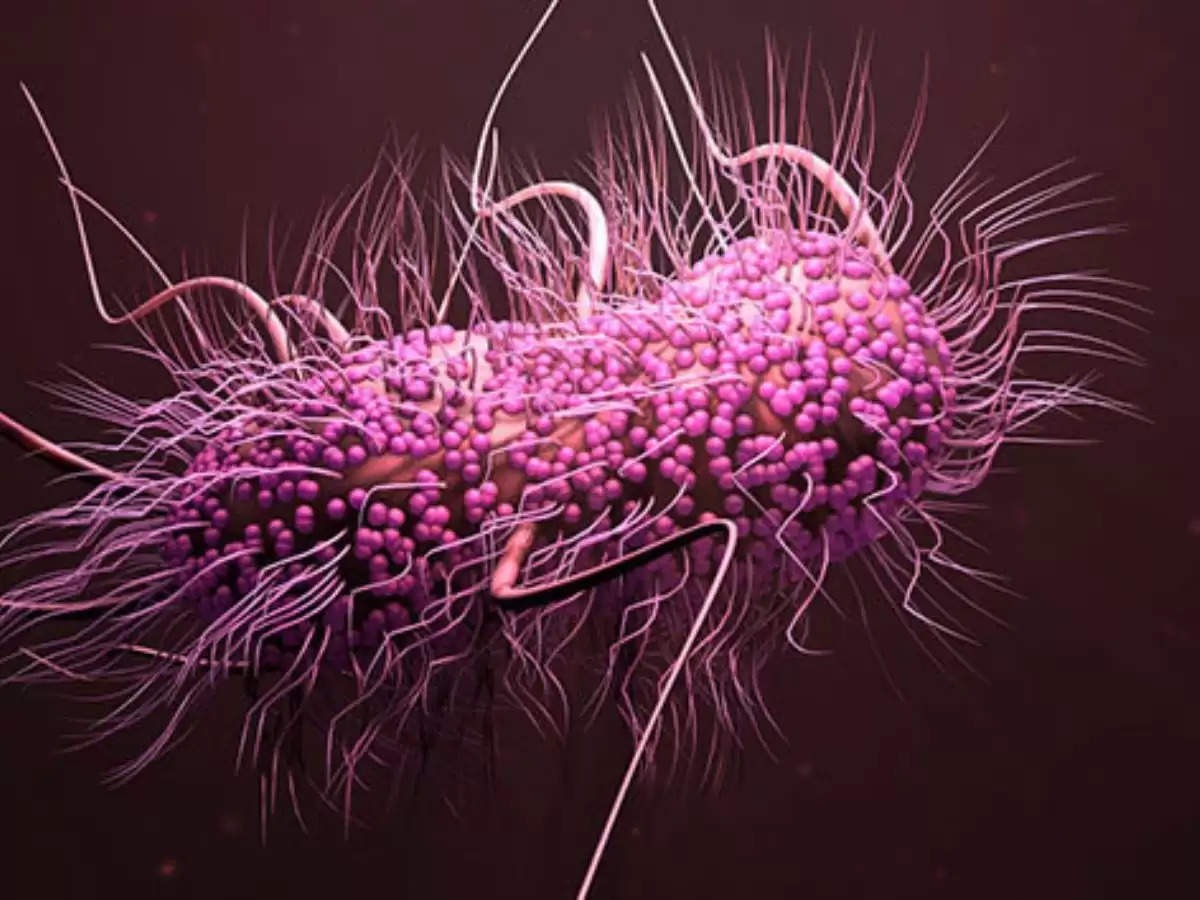
A new report has revealed something shocking. According to the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), the dangerous presence of superbugs has been observed in 21 major hospitals of the country. These superbugs can pose a threat to the lives of patients admitted in hospitals. Superbugs (Klebsiella pneumonia and Escherichia coli) classified by the World Health Organization (WHO) were found mainly in AIIMS Delhi, PGI Chandigarh, Apollo Hospital Chennai and Gangaram Hospital in Delhi, among many other hospitals.
The ICMR report said that these superbugs were found in samples including blood, urine and other fluids of patients, which were collected from outpatient departments (OPDs), wards and ICUs. This revelation has rung alarm bells in hospitals and they have been advised to follow strict protocols for better management of medicines and disposal of bacterial waste to prevent further spread of the superbug.
Could superbugs be as big a threat as cancer?
A report published earlier this year by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) said that superbugs could become as big a threat as cancer by 2050. The report said that the direct economic consequences of such superbugs would be about $3.4 trillion per year by the end of 2030. In addition, 24 million people could be pushed into extreme poverty. The report said that pollution by animal husbandry and pharmaceutical companies has increased the emergence of superbugs.
What are superbugs?
Superbugs are strains of bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites that are resistant to most antibiotics, including modern medicines. They are often caused by the misuse of antibiotics. Disinfectants, antiseptics and antibiotics that can help germs grow stronger are present everywhere, from toothpaste and shampoo to cow's milk and dirty water.
There are two main types of superbugs:
They become antimicrobial resistant (AMR) mainly in two ways. First is the excessive use of drugs in animal husbandry which provides bacterial strains with an opportunity to mutate to escape the effect of any antibiotic. Second, pharma companies pollute waterways. Drug companies do not treat medical waste properly which leads to the creation of resistant superbugs. AMR is a natural phenomenon as experts call it 'genetic capitalism'. However, the excessive use of drugs, especially antibiotics, has accelerated this process.
 look news india
look news india