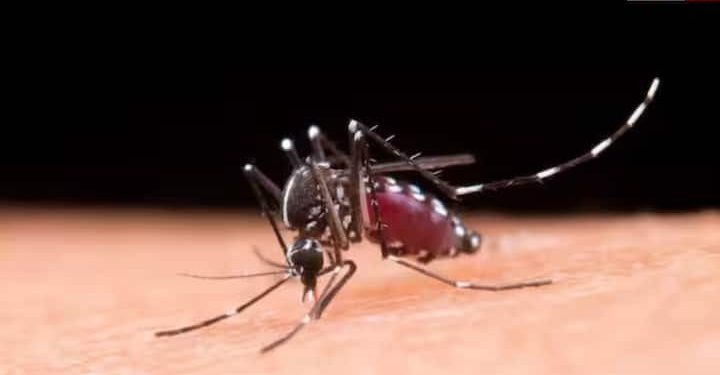
Mosquito breeding increases rapidly during monsoon. Dengue outbreak is increasing in Karnataka, Kerala and Maharashtra. But if we are aware, we can control this disease. Dengue fever includes sudden fever, severe headache, pain behind the eyes, muscle and joint pain, nausea, vomiting, swollen glands and rash. These symptoms usually appear 4-10 days after mosquito bite and can last for 2-10 days.
This can quickly turn into severe dengue, also called dengue hemorrhagic fever or dengue shock syndrome, when the number of clot-forming cells (platelets) in your bloodstream drops and your blood vessels become so damaged that they leak. This can lead to shock, internal bleeding and organ failure.
If you are experiencing dengue symptoms, get a dengue NS1 antigen test, which measures the non-structural proteins of the virus, or a PCR test. Then get an IgM antibody test on the fourth or fifth day, when you are more likely to have dengue.
If you experience the symptoms mentioned above, get a complete blood count (CBC) done and if positive, repeat it every other day to check the platelet levels.
One of the most important markers is PCV (packed cell volume), which is a measure of the viscosity of the blood. It indicates an increase in red blood cells or dehydration.
 look news india
look news india
