After two decades i.e. 20 years, the most powerful solar storm hit the Earth on Friday. Due to which the sky has been seen shining from America to Britain. America's National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has classified this magnetic storm in the G5 category. Geomagnetic storms are measured on a scale from G1 to G5, with G5 considered the most extreme level of storm. NOAA has warned that this geomagnetic storm coming from the Sun could affect satellites and power grids on Earth. Due to which communication may be disrupted and many areas may be plunged into darkness.
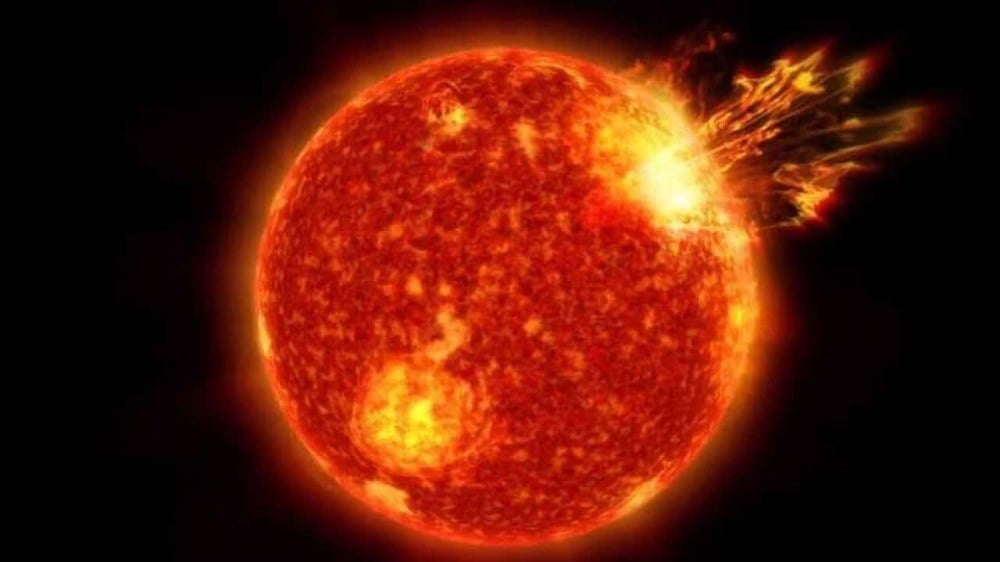
NASA took a picture of the shining sun
The Solar Dynamics Observatory of the American space agency NASA has captured the picture of this explosion in the Sun. The Sun emitted a bright flash on May 10, 2024, which peaked at 2:54 a.m. local time, NASA said. According to NOAA's Weather Prediction Center, the increase in solar flares has resulted in numerous ejections of plasma and magnetic fields from the corona (coronal mass ejections). Earlier in October 2003 there was a major solar storm, which caused blackouts in Sweden and damaged electricity infrastructure in South Africa. Scientists expect more coronal mass ejections to hit Earth in the coming days.
Earth's equivalent position in the Sun
Every 11 years the Sun experiences low and high levels of solar activity linked to the amount of sunspots on its surface; the Sun's strong and constantly changing magnetic field drives these dark areas. Some of these may be Earth-sized or even larger. Geomagnetic storms have led to a sharp increase in the Northern Lights, which have been seen from the US to Britain. During the solar cycle the Sun changes from calm to intense and active periods. The peak of activity is called solar maximum. During the peak of this motion in the Sun, the Sun's magnetic poles reverse. The Sun's current run, called Solar Cycle 25, is full of more activity than expected. Scientists have tracked more sunspots this time than in previous cycles.
What will be the effect on the earth?
Intense solar flares create a strong geomagnetic field, which disrupts part of Earth's upper atmosphere. This could have immediate effects on communications and GPS. Along with this, the unlimited energy emanating from the Sun can also disrupt the electronics of the spacecraft. Astronauts may be affected for anywhere from 20 minutes to several hours.
There is no threat to the International Space Station
After a thorough analysis of the solar storm, NASA has said that it poses no threat to the crew aboard the International Space Station and no additional precautionary measures are needed. NASA said Earth's magnetic field protects life on the planet from radiation coming from space. However, the space station orbits about 400 kilometers above Earth. However, it enjoys some protection due to its proximity to the Earth's magnetic field. It takes 8 minutes for a solar flare to reach Earth, meaning the most recent flare has passed. This increased illumination poses no danger to the crew.
 look news india
look news india