Science News: Supply of electricity from space to Earth? If you had said this a few years ago, even scientists would have started laughing. But now it is not so. Many countries including America, China, Japan are moving towards achieving such capability in the coming years. A British startup is also going to supply electricity to the Earth through satellites in space by 2030. This company wants to start supplying electricity to Iceland by sending the first demonstrator satellite by 2030. If successful, this will be the first instance of this renewable energy source in the world.
How will electricity be supplied from space to Earth?
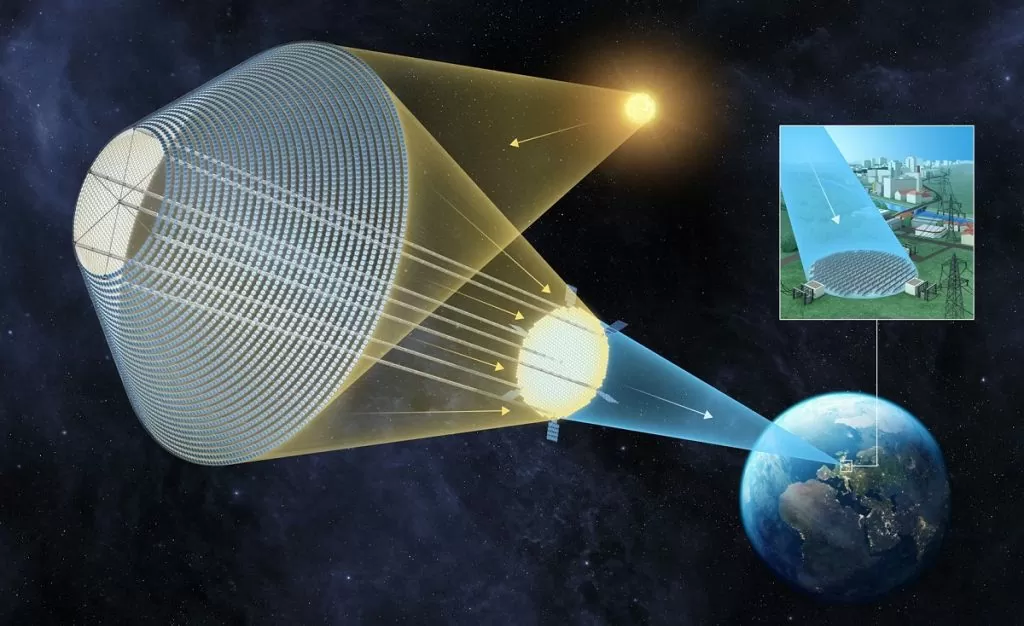
The space solar power project is a partnership between the UK's Space Solar, Reykjavik Energy and Iceland's sustainability initiative Transition Labs. The company is planning to launch the first satellite in the next six years which will beam 30 MW of clean energy to Earth. This much electricity can light about 3,000 houses. Energy from the satellite will be sent in the form of high frequency radio waves. Receiving antennas installed on the ground will collect this energy, convert it into electricity and send it to the power grid.
No matter what the weather, there will be 24×7 power supply from space.
This satellite will be approximately 400 meters wide including solar panels. According to the report, the weight of the satellite could be 70.5 tonnes. It will revolve around the planet in a medium Earth orbit. This orbit is a near-space region at an altitude of 2,000 to 36,000 kilometers.
The partnership aims to build a fleet of six such space-based solar power stations by 2036. This fleet will be able to supply several gigawatts of clean electricity to people on Earth 24×7, regardless of the weather. By the mid-2040s, these power plants in space may be able to supply more than 15 gigawatts of energy.
How much will it cost? there will be no mistake
According to Space Solar, the first power plant will cost $800 million to build. The company said the system would provide electricity at about one-fourth the cost of nuclear power, or $2.25 billion per gigawatt.
Unlike photovoltaics and wind turbines on Earth, satellite power plants will not have problems with intermittent power generation. This is a major drawback of traditional renewable energy generation. These satellites will produce power continuously regardless of the time of day or weather conditions.
Musk's company will take this satellite
According to the plan created by Space Solar, each 30-MW solar farm would be delivered to orbit in a single launch by SpaceX's Starship megarocket. SpaceX is the aerospace company of the world's richest man, Elon Musk. With the ability to carry up to 165 tons of payload into low Earth orbit, Starship has significantly reduced launch costs.
 look news india
look news india
